Compare Clouds - Part 1

Introduction
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses operate and has become the backbone of modern digital infrastructure. The ability to access vast computing resources, store data securely, and leverage scalable solutions has propelled the adoption of cloud platforms. Among the major players in the cloud computing market, three giants stand out: Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). In this blog post, we will delve into a comprehensive comparison of these leading cloud platforms, exploring their strengths, features, and capabilities.
The increasing reliance on cloud services has made it crucial for organizations to select the right cloud platform that aligns with their specific needs. AWS, with its extensive range of services and its early entry into the market, has long been considered a dominant force. Azure, backed by Microsoft's expertise and vast enterprise ecosystem, has rapidly gained traction, especially among businesses that heavily rely on Microsoft technologies. GCP, driven by Google's innovation and robust infrastructure, has also made significant strides, attracting businesses with its machine learning and data analytics capabilities.
Understanding the key differences and nuances between these cloud platforms is vital for businesses, developers, and technology enthusiasts alike. By comparing AWS, Azure, and GCP, we can gain insights into their strengths and weaknesses, enabling informed decision-making when it comes to choosing the right cloud provider.
Throughout this blog post, we will examine various aspects, including pricing structures, services and features, scalability and performance, integration capabilities, security measures, and customer use cases. By evaluating these factors, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview of each cloud platform, empowering readers to make informed decisions based on their unique requirements.
So, whether you are a startup looking for cost-effective solutions, an enterprise seeking seamless integration, or a data-driven organization requiring advanced analytics capabilities, this comparison will help you navigate the intricate world of cloud computing. Let's dive in and explore the fascinating landscape of AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud Platform.
Brief Overview of Each Cloud Platform
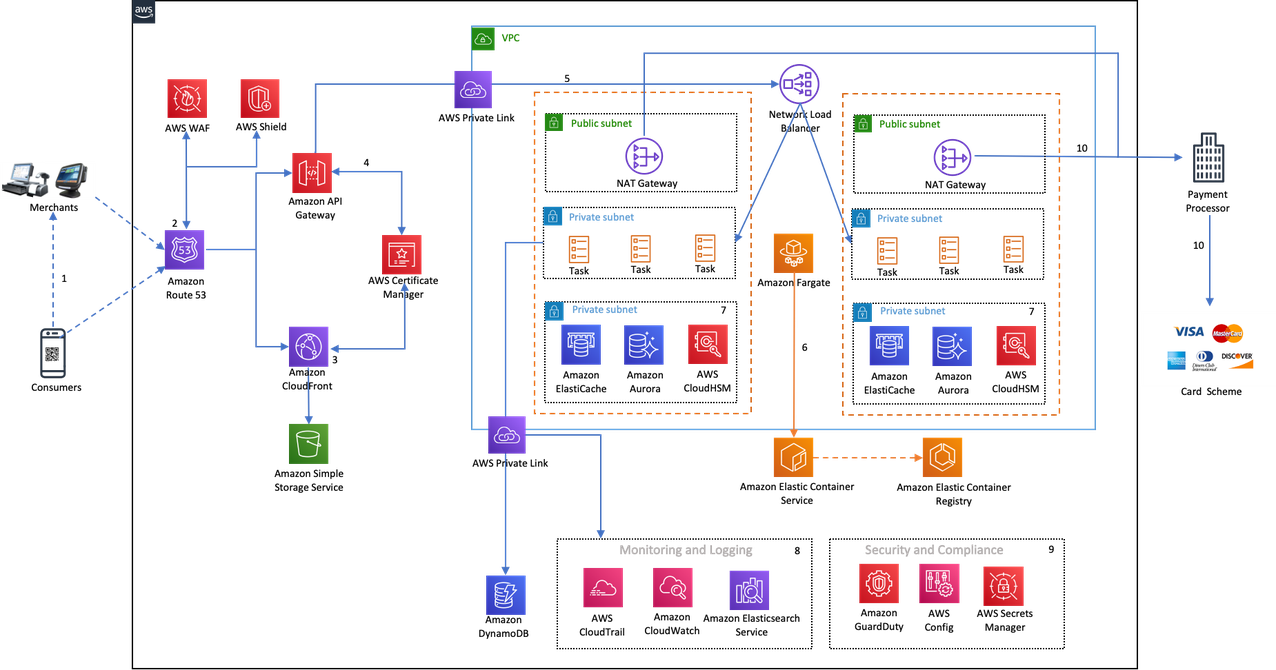
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is the undisputed leader in the cloud computing market, offering a comprehensive suite of services and an expansive global infrastructure. AWS was one of the pioneers in cloud services, launching in 2006, and has since become a go-to choice for organizations of all sizes. It provides a robust set of solutions for computing power, storage, databases, analytics, machine learning, and more.
With AWS, customers have access to a vast array of services, including Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) for scalable virtual servers, Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) for secure and durable object storage, Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) for managed databases, and Amazon Redshift for data warehousing. AWS also offers additional services like AWS Lambda for serverless computing, Amazon Sagemaker for machine learning, and Amazon CloudFront for content delivery.
One of the significant advantages of AWS is its global presence, with regions and availability zones distributed worldwide, ensuring low-latency and high availability for applications. AWS has a mature ecosystem with extensive documentation, strong community support, and a wide range of third-party integrations. Its pay-as-you-go pricing model allows customers to pay only for the resources they consume, providing cost flexibility.
Microsoft Azure
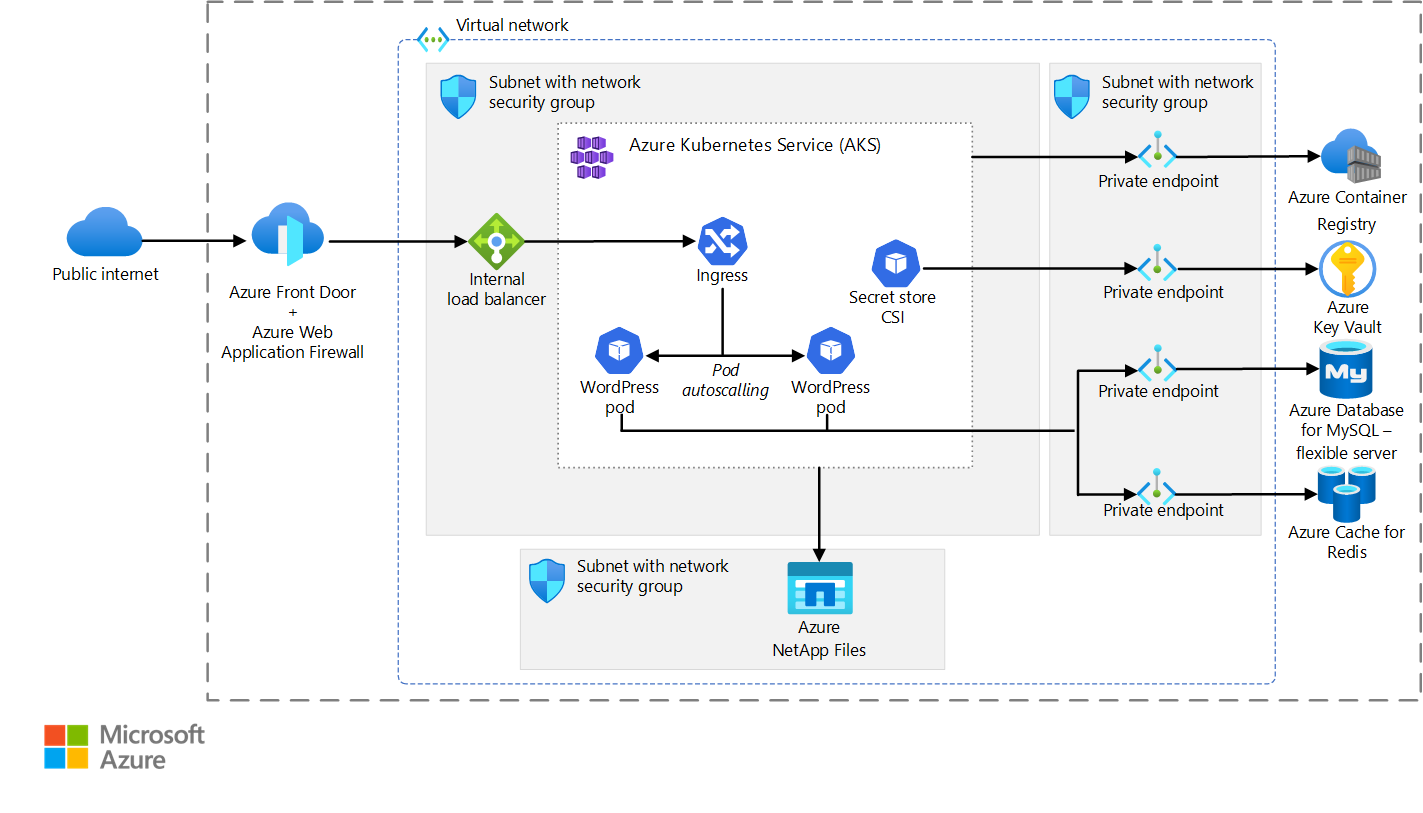
Microsoft Azure is a cloud computing platform offered by Microsoft. It has gained substantial market share due to its integration with Microsoft's existing enterprise technologies and its ability to cater to hybrid cloud environments. Azure provides a broad range of services for computing, storage, databases, networking, AI, and more, making it a comprehensive cloud solution for businesses.
Azure offers services like Azure Virtual Machines for scalable computing resources, Azure Blob Storage for object storage, Azure SQL Database for managed databases, and Azure Cosmos DB for globally distributed databases. It also includes services like Azure Functions for serverless computing, Azure Machine Learning for AI and ML capabilities, and Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) for container orchestration.
One of Azure's strengths lies in its seamless integration with Microsoft's ecosystem, including Windows Server, Active Directory, and popular development tools like Visual Studio. Azure's hybrid capabilities allow businesses to extend their on-premises infrastructure to the cloud, ensuring a smooth transition. Azure also boasts a robust global network of data centers, ensuring low-latency connectivity across regions.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
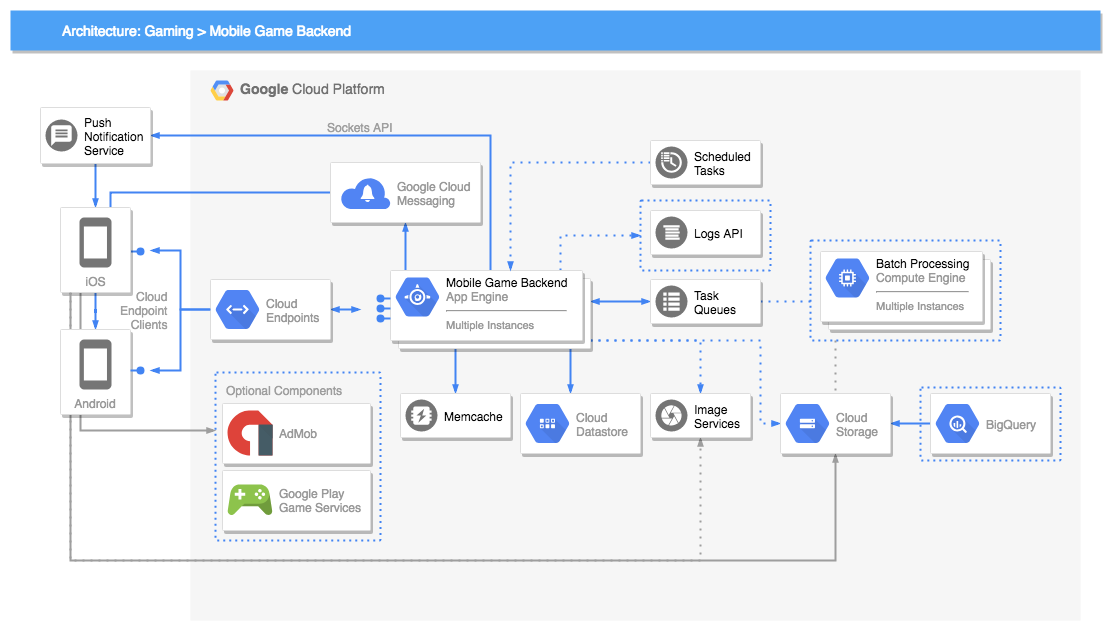
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is Google's cloud computing offering, known for its focus on data analytics, machine learning, and containerized workloads. GCP provides a wide range of services, including computing, storage, databases, AI, and networking, with a strong emphasis on data-centric applications.
GCP offers services like Google Compute Engine for scalable VMs, Google Cloud Storage for object storage, Cloud SQL for managed databases, and BigQuery for serverless analytics. It also includes services like Google Cloud Functions for serverless computing, AI Platform for machine learning, and Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) for container orchestration.
What sets GCP apart is its expertise in data analytics and machine learning. It provides specialized services like Google BigQuery for high-speed, fully-managed data warehousing, and Google Cloud AI for pre-trained machine learning models. GCP also leverages Google's global network infrastructure for high-performance and secure connectivity.
Each cloud platform has its unique strengths and target audiences. Understanding their core offerings and areas of expertise will help businesses make informed decisions when selecting a cloud provider. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into various aspects like pricing, services, scalability, integration, security, and customer use cases for AWS, Azure, and GCP.
Pricing and Cost Structure
Pricing is a crucial consideration when selecting a cloud platform, as it directly impacts the operational costs of businesses. Let's explore the pricing models and cost structures of AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) to understand how they differ.

Amazon Web Services (AWS)
AWS offers a flexible and pay-as-you-go pricing model, allowing customers to pay only for the resources they utilize. It offers various pricing dimensions, including compute instances, storage, network data transfer, and additional services. AWS provides an online calculator called the AWS Simple Monthly Calculator, which helps estimate the costs based on resource usage and service selection.
AWS offers different pricing options to accommodate diverse business needs. These options include On-Demand Instances, where customers pay for compute capacity by the hour with no long-term commitments, Reserved Instances, which offer significant discounts for long-term commitments, and Spot Instances, where customers bid for unused EC2 instances at reduced prices. AWS also provides savings plans and volume discounts for sustained usage and specific services.
Microsoft Azure
Azure follows a similar pay-as-you-go pricing model, with pricing based on resource consumption. It provides a Pricing Calculator that helps estimate costs based on factors like virtual machines, storage, networking, and additional services.
Azure offers various pricing options to optimize costs. It includes Pay-As-You-Go, where customers are billed on an hourly basis, and Reserved Instances, which provide substantial discounts for long-term commitments. Azure also offers Spot Virtual Machines, similar to AWS Spot Instances, where customers can bid for unused capacity at discounted prices. Azure Hybrid Benefit allows customers with existing Microsoft licenses to apply them to Azure services, providing cost savings. Additionally, Azure provides various cost management and optimization tools to monitor and control spending.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
GCP adopts a similar pricing model, with pay-as-you-go billing based on resource consumption. GCP provides a Pricing Calculator that allows customers to estimate costs based on services and usage patterns.
GCP offers several pricing options to meet different business requirements. It includes On-Demand pricing, where customers pay for resources based on usage, and Committed Use Contracts, which offer significant discounts for sustained usage over one or three years. GCP's Preemptible VMs are similar to AWS Spot Instances and Azure Spot Virtual Machines, providing lower-cost resources that can be interrupted with short notice. GCP also offers sustained use discounts for long-running workloads and provides tools for cost management and optimization.
It's important to note that the pricing structures and specific costs can vary based on regions, service types, and usage patterns. Organizations should carefully analyze their anticipated usage and requirements to estimate costs accurately.
When comparing the pricing of these cloud platforms, it's essential to consider factors beyond just the listed prices. These include the availability of discounts, contract terms, support options, and the overall value delivered by the services.
In the next sections, we will explore the services and features offered by AWS, Azure, and GCP, allowing us to gain a comprehensive understanding of each platform's capabilities.

